Glycan Analysis and Advisory Services
Role and importance of glycosylation
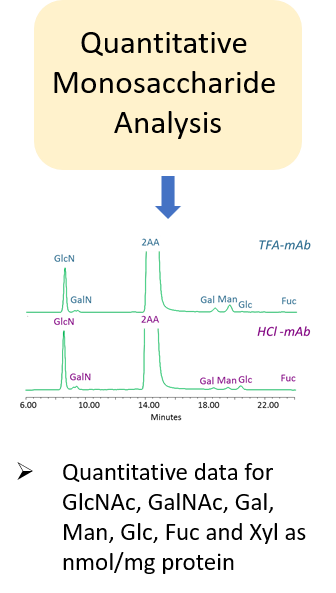
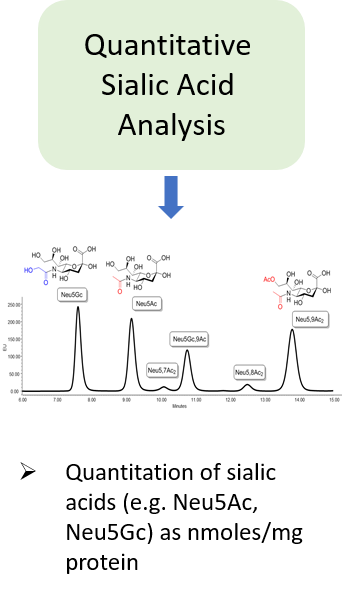
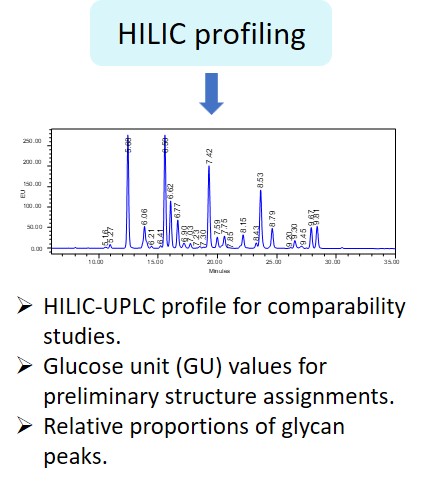
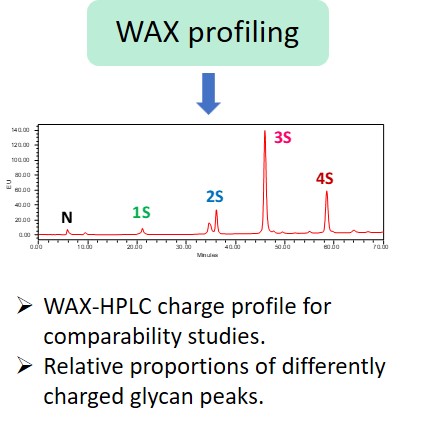
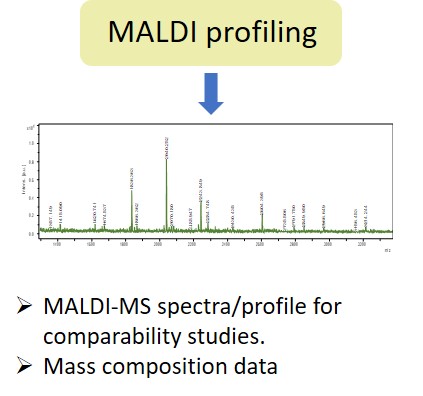
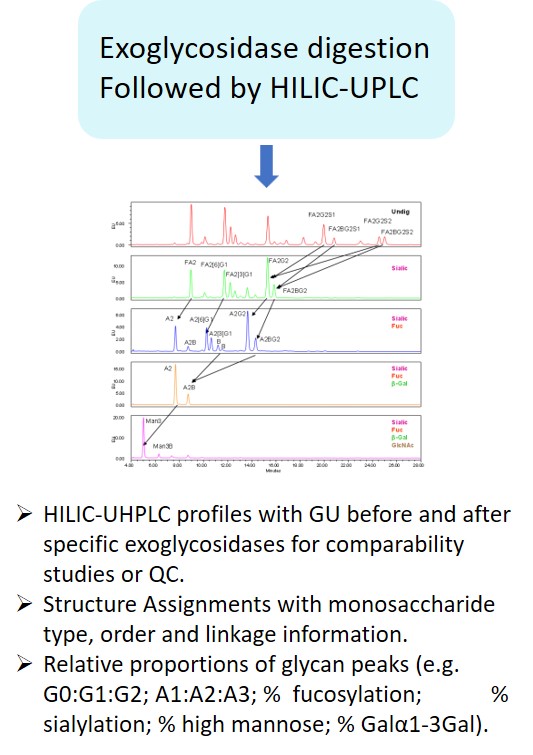
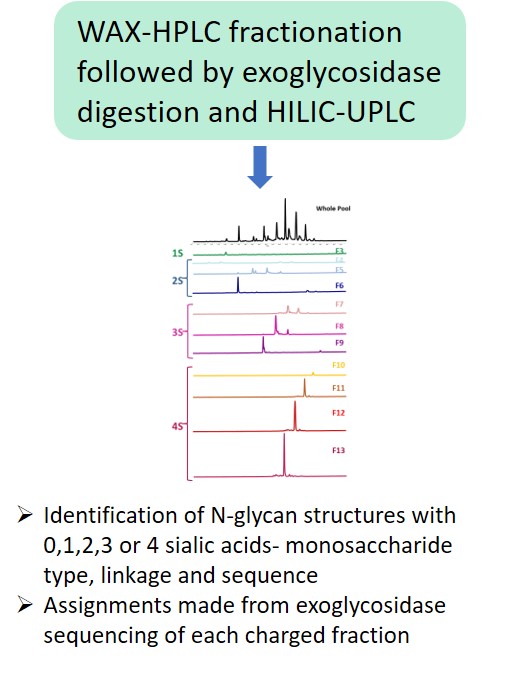
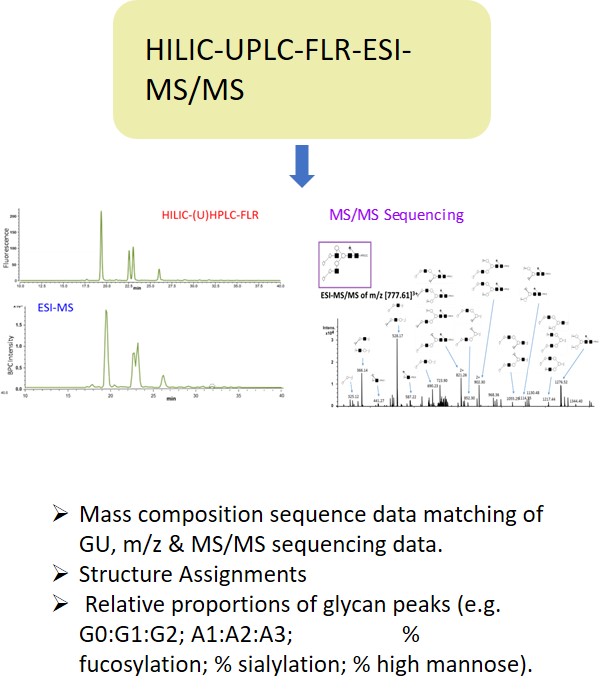
Glycosylation is a post-translational modification which plays an important role in the bioactivity, stability, and immunogenicity of therapeutic glycoproteins. Unlike transcription, it is a non-template-driven process whose outcomes are highly variable. Given its impact on drug safety, regulators classify glycosylation as a Critical Quality Attribute of biopharmaceuticals. Therefore, manufacturers are required to monitor and control it at every stage of the drug manufacturing process.
Regulatory delays due to non-compliant reporting as well as out-of-spec batch failures can lead to significant financial losses. This is something our expert team can help you with. We have extensive experience in glycan analysis including glycoconjugates, biopharmaceuticals and biological specimens.
Sample types
Ludger has over 20 years of expertise with analysing glycosylation (including N- and O- glycosylation) from a variety of sample types including:

Biopharmaceuticals: monoclonal antibodies (mAbs), Fc fusion proteins,
vaccines, and glycoprotein hormones such as follicle stimulating hormone (FSH), and erythropoietin (EPO).

Cells: mammalian cell lines, bacterial cell components
Biological samples: patient’s plasma, fluids, tissues and others
Infected samples and cell lines: COVID-19 patient samples and cell lines
We listen and respond with dedicated tailored solutions. Our data and customised reports are used:
- in QbD studies and early stages of drug development
- in process optimisation and production scale-up
- in comparability studies (biosimilars, biobetters)
- to support regulatory submissions
- for lot release of drug batches during biomanufacturing
- in research & method development
Our philosophy is to work with you in a partnership to ensure the successful delivery of the information you need.