procainamide glycan labelling kit (2PB reductant)
Procainamide labelling: A reliable and flexible approach to glycan analysis
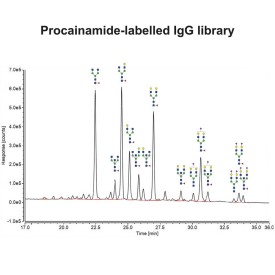
Procainamide labelling permits glycan identification by either mass spectrometry or (U)HPLC, and because of its improved ionisation efficiency compared to 2AB labelling it can permit identification of minor glycans (<1% relative peak area) by ESI-MS.
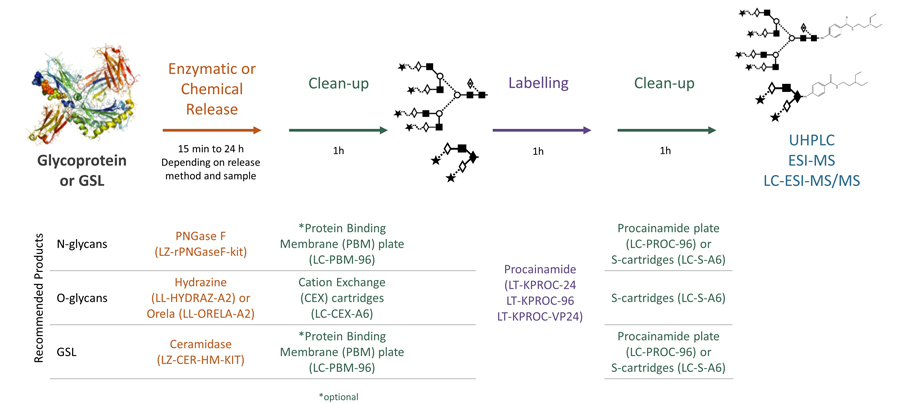
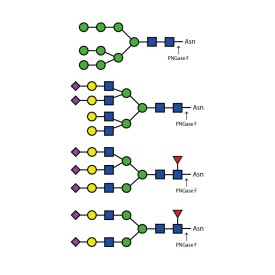
Ludger's procainamide labelling system is suitable for N-glycans, O-glycans, GSL-glycans, heparin or any sugar with a reducing terminus. Also, once labelled with procainamide the glycans can be incubated with exoglycosidases.
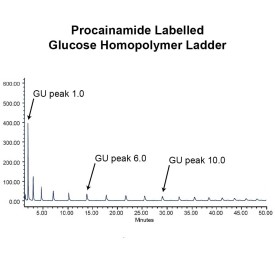
As well as labelling kits we offer a clean up system for use after labelling and a range of procainamide labelled glycan standards (including an N-glycan library and glucose homopolymer ladder). Using products together (including LudgerZyme PNGaseF, LZ-rPNGaseF-kit), N-glycan sample preparation can be carried out in one day (for 96 samples)

Features and Benefits - Quick Links:
Workflow
LudgerTag Procainamide for glycan profiling and identification:
Application Note
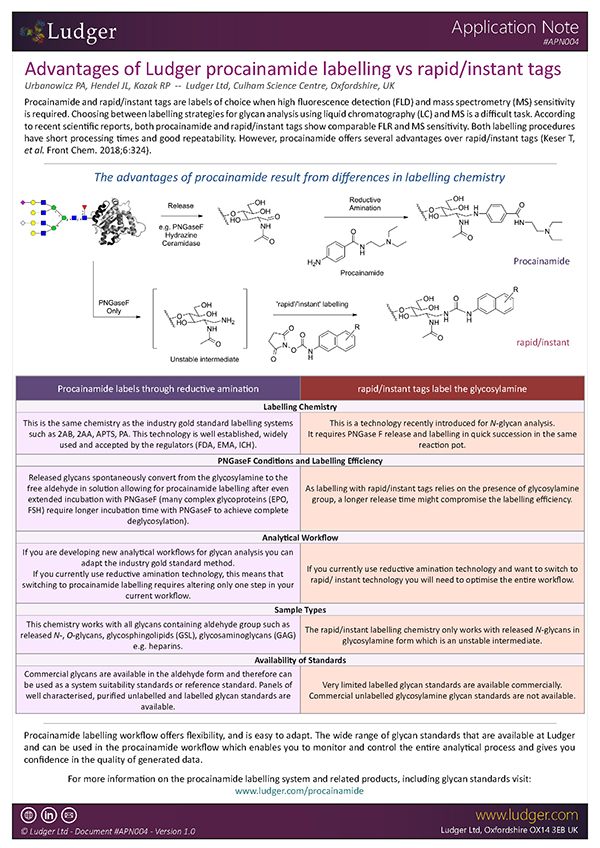
Advantages of Ludger procainamide labelling vs rapid/instant tags
Choosing between labelling strategies for glycan analysis using liquid chromatography with fluorescence detection (LC-FLR) and mass spectrometry (MS) is a difficult task. Even though 2-aminobenzamide (2-AB) labelling has been a gold standard method for glycan profiling and characterisation using LC-FLR as an analytical platform, new contenders such as procainamide and rapid/instant tags have been in use recently due to their comparable fluorescence, increased MS sensitivity and short processing times (Keser T, et al. Front Chem. 2018;6:324).
However, it should be noted that procainamide labelling offers several advantages over rapid/instant tags. Our new application note outlines the features, benefits and advantages of Ludger's Procainamide labelling technology in comparison to gold standard labelling (2-AB) as well as other rapid/instant tags.
 Click for pdf version of application note
Click for pdf version of application note
Comparison Table
The table below provides a quick summary of the features and benefits of Ludger's procainamide labelling technology in comparison to competitor offerings:
| Ludger Procainamide | Rapid/instant labelling* | |
|---|---|---|
| Sensitive fluorescence detection for relative glycan quantitation by (U)HPLC | ✓✓✓✓✓ | ✓✓✓✓✓ |
| Sensitive ESI-MS and MS/MS detection for glycan structural analysis | ✓✓✓✓✓ | ✓✓✓✓✓ |
| Sample processing speed | ✓✓✓ | ✓✓✓✓✓ |
| Can label purified glycans and standards? | YES | NO |
| Use for O-glycans? | YES | NO |
| Use for GSL glycans? | YES | NO |
| Similar glycan derivatisation chemistry to 2-AB industry standard? | YES | NO |
| Suitable for exoglycosidase sequencing? | YES | Fluorophore dependent** |
Related Ludger Publications & Posters
Complex N-glycan breakdown by gut Bacteroides involves an extensive enzymatic apparatus encoded by multiple co-regulated genetic loci
Briliūtė J, Urbanowicz PA, Luis AS, Baslé A, Paterson N, Rebello O, Hendel J, Ndeh DA, Lowe EC, Martens EC, Spencer DIR, Bolam DN, Crouch LI.
Nature Microbiology. 2019 Jun 3.
doi: 10.1038/s41564-019-0466-x
Engineering and stable production of recombinant IgE for cancer immunotherapy and AllergoOncology.
Crescioli S, Chiaruttini G, Mele S, Ilieva KM, Pellizzari G, Spencer DIR, Gardner RA, Lacy KE, Spicer JF, Tutt ANJ, Wagner GK, Karagiannis SN.
Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology. 2018 Apr;141(4):1519-1523.e9.
doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2017.12.986
Analysis of Three Epoetin Alpha Products by LC and LC-MS Indicates Differences in Glycosylation Critical Quality Attributes, Including Sialic Acid Content.
Thomson RI, Gardner RA, Strohfeldt K, Fernandes DL, Stafford GP, Spencer DIR, Osborn HMI.
Analytical Chemistry. 2017 Jun 20;89(12):6455-6462.
doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.7b00353

Variation of Human Salivary O-Glycome.
Kozak RP, Urbanowicz PA, Punyadeera C, Reiding KR, Jansen BC, Royle L, Spencer DI, Fernandes DL, Wuhrer M.
PLoS One. 2016 Sep 9;11(9):e0162824.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0162824
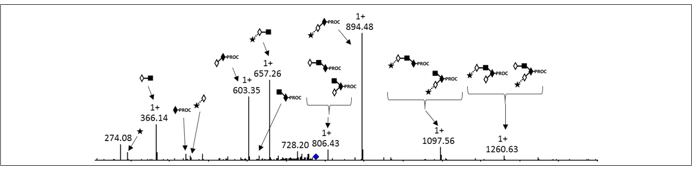
Comparison of procainamide and 2-aminobenzamide labeling for profiling and identification of glycans by liquid chromatography with fluorescence detection coupled to electrospray ionization-mass spectrometry.
Kozak RP, Badía Tortosa C, Fernandes DL, Spencer DI.
Analytical Biochemistry. 2015 Oct 1;486:38-40.
doi: 10.1016/j.ab.2015.06.006
Investigating the role of insect vector glycosylation in African sleeping sickness transmission: Characterisation of procainamide-labelled tsetse fly saliva N-glycans
Kozak RP, Wongtrakul-Kish K, Williams C, Fernandes DL, Perally S, Rose C, Spencer DI, Acosta-Serrano A
Presented at Glyco23: 23rd International Symposium on Glycoconjugates
Split, Croatia, September 2015
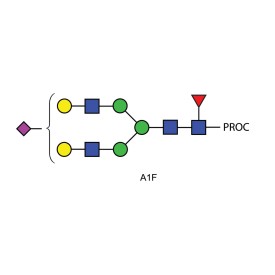
Procainamide labelling as part of a flexible glycoprofiling system for monitoring of Gal-a1-3Gal related Glycosylation Critical Quality Attributes (GCQAs) of monoclonal antibody (mAb) therapeutics throughout the product life cycle
Kozak RP, Royle L, Liew LP, Spencer DI, Fernandes DL
Presented at WCBP 2016: 20th Symposium on the Interface of Regulatory and Analytical Sciences for Biotechnology Health Products
Washington DC, United States, January 2016
A QbD-compatible approach for reliable measurement of sialic acid O-acetylation as a potential Glycosylation Critical Quality Attribute (GCQA) of erythropoietin (EPO) therapeutics
Fernandes DL, Thomson R, Gardner R, Liew LP, Kozak RP, Royle L, Strohfeldt K, Osborn H, Spencer DI
Presented at WCBP 2016: 20th Symposium on the Interface of Regulatory and Analytical Sciences for Biotechnology Health Products
Washington DC, United States, January 2016
![]() For labelling of free glycans with procainamide (PROC) 2-picoline borane reductant. Kit sufficient for 24 samples.
For labelling of free glycans with procainamide (PROC) 2-picoline borane reductant. Kit sufficient for 24 samples.
Kit contents:
Each kit is suitable for labelling 24 samples (N- and O-glycans) and contains the following components:
- Procainamide dye (LT-PROC-01)
- 2PB reductant (2-picoline borane) (LT-PB-01)
- 30% acetic acid in DMSO (LT-ACETIC-DMSO-01
Specifications for LT-KPROC-VP24
Application: For labeling of free glycans with procainamide (PROC).
Description The kit contains reagents for the conjugation of dye to the free reducing end of the glycan by a reductive amination reaction
Dye Properties Mass free dye = 235.33. Fluorescence, λex = 310 nm, λem = 370 nm.
Number of Samples 12 separate analytical samples per set of labeling reagents (24 samples in total for the kit)
Amount of Sample From 25 pmol up to 25 nmol glycans per sample.
Suitable Samples Any purified glycans with free reducing termini can be labeled.
Structural Integrity No detectable (< 2 mole per cent) loss of sialic acid, fucose, sulfate, or phosphate.
Labeling Selectivity Essentially stoichiometric labeling.
Storage: Store at room temperature in the dark. Protect from sources of heat, light, and moisture. The reagents are stable for at least two years as supplied.
Shipping: The product can be shipped at ambient temperature.
Handling: Ensure that any glass, plasticware or solvents used are free of glycosidases and environmental carbohydrates. Use powder-free gloves for all sample handling procedures and avoid contamination with environmental carbohydrate.
All steps involving labeling reagents must be performed in a dry environment with dry glassware and plasticware. Once individual vials of reagents are opened, their contents should be used immediately and excess then discarded according to local safety rules.
Safety: For research use only. Not for human or drug use
Please read the Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDS's) for all chemicals used. All processes involving labeling reagents should be performed using appropriate personal safety protection - eyeglasses, chemically resistant gloves (e.g. nitrile), etc. - and where appropriate in a laboratory fume cupboard.

















-275x275.jpg)
-275x275.jpg)
-275x275.jpg)
-275x275.jpg)
-275x275.jpg)
-275x275.jpg)
-275x275.jpg)
-275x275.jpg)
-275x275.jpg)
-275x275.jpg)
-275x275.jpg)