Exoglycosidases
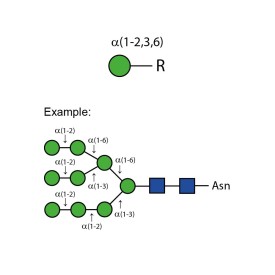
α-(1-2,3,6) mannosidase
E-AM01
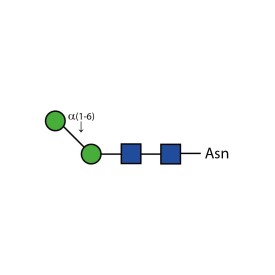
α-(1,6) core mannosidase
E-AM02
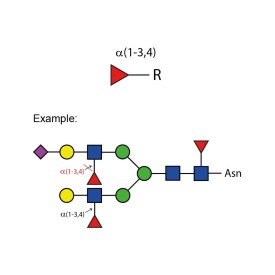
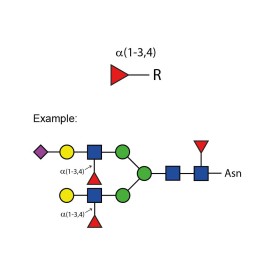
α-(1-3,4) fucosidase
E-F134
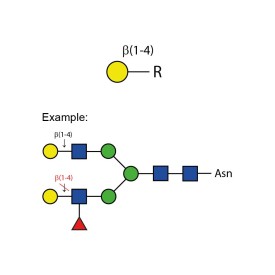
β-(1-4)-galactosidase
E-BG07
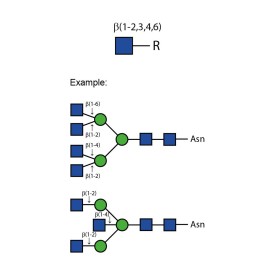
β-N-acetylglucosaminidase
E-GL01
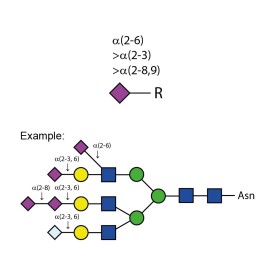
Sialidase Au α-(2-3,6,8,9)
E-S001
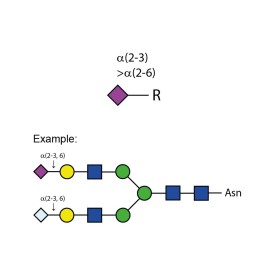
Sialidase Cp α-(2-3,6)
E-S005
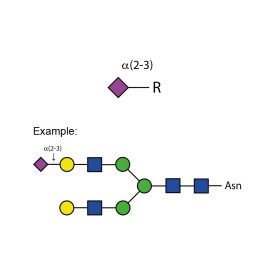
Sialidase Sp α-(2-3)
E-S007
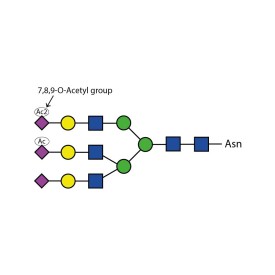
Sialate O-acetylesterase kit
LZ-ACASE-KIT
LudgerZyme α(1-3,4) fucosidase kit
LZ-FUCOSIDASE-01-KIT
Showing 1 to 10 of 10 (1 Pages)