N-Glycolylneuraminic Acid Quantitative Standard
References:
Fernandes, D. Biopharmaceutical Sialylation. European Biopharmaceutical Review. Spring 2006. pp 100 -104
Bhide GP, Colley KJ. Sialylation of N-glycans: mechanism, cellular compartmentalization and function. Histochem Cell Biol. 2017 Feb;147(2):149-174. doi: 10.1007/s00418-016-1520-x. Epub 2016 Dec 14.
Anumula KR. Rapid quantitative determination of sialic acids in glycoproteins by high-performance liquid chromatography with a sensitive fluorescence detection. Analytical Biochemistry 230: pp24-30, 1995,
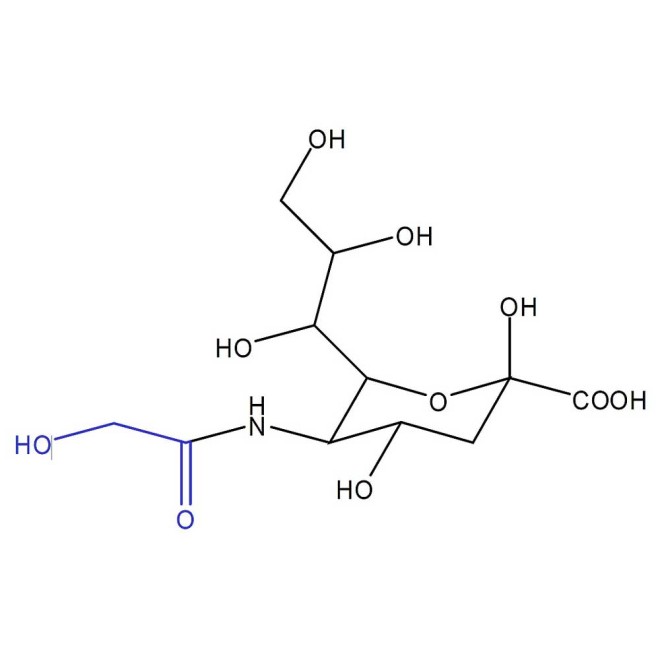
The NGNA standard (N-glycolylneuraminic acid or Neu5Gc) standard is a quantitative standard of NIST-F and USP traceable Neu5Gc monosaccharide.
It is also supplied as a component of our LudgerTag DMB sialic acid release and labelling kit (LT-KDMB-A1).
View product documentation
Ludger Guides to Sialic Acid Analysis:
 Sialylation Guide I: Neu5Ac and Neu5Gc Quantitation
Sialylation Guide I: Neu5Ac and Neu5Gc Quantitation
 Sialylation Guide II: Highly Sialylated Glycoproteins
Sialylation Guide II: Highly Sialylated Glycoproteins
 Application Note: Quantitative Sialic Acid Analysis
Application Note: Quantitative Sialic Acid Analysis
Product Specification
N-glycolylneuraminic acid (NGNA) standard
The NGNA standard (N-glycolylneuraminic acid or Neu5Gc) standard is a quantitative standard of NIST-F and USP traceable Neu5Gc monosaccharide. The N-acetolylneuraminic acid quantitative standard (Neu5Ac or NANA) is also available.
Form: Dry. Dried by centrifugal evaporation from an aqueous solution.
Amount Supplied:
CM-NEU-GC-01 1 nmol
Storage: -20˚C both before and after dissolution. This product is stable for at least 5 years as supplied.
Shipping: The NGNA standard can be shipped at ambient when dry. After dissolution, ship on dry ice.
Handling: Allow the unopened vial to reach ambient temperature and tap unopened on a solid surface to ensure that most of the lyophilized material is at the bottom of the vial. Gently remove the cap, add the desired volume of reconstitution medium, re-cap and mix thoroughly to bring all the oligosaccharides into the solution. For maximal recovery of oligosaccharide, ensure that the cap lining is also rinsed and centrifuge the reconstituted vial briefly before use. Ensure that any glass, plasticware or solvents used are free of glycosidases and environmental carbohydrates. Minimise exposure to elevated temperatures or extremes of pH. High temperatures and low pH will cause desialylation. High pH will cause epimerisation of the reducing terminus GlcNAc.
Safety: This product is non-hazardous and has been purified from natural sources certified to be free of all hazardous material including pathogenic biological agents.